Are you interested in investments? Specifically, have you ever wondered how monetary stimuli, such as quantitative easing, impact the price of precious metals like gold? Well, hold onto your seats because today we are going to dive deep into this fascinating subject. As an experienced investor in gold, I have witnessed firsthand how these monetary policies can cause significant fluctuations in the market. So, buckle up and get ready to uncover the intricate relationship between quantitative easing and gold, and how it can potentially affect your investment portfolio. Get ready to be amazed!
This image is property of www.physicalgold.com.
What is Quantitative Easing (QE)?
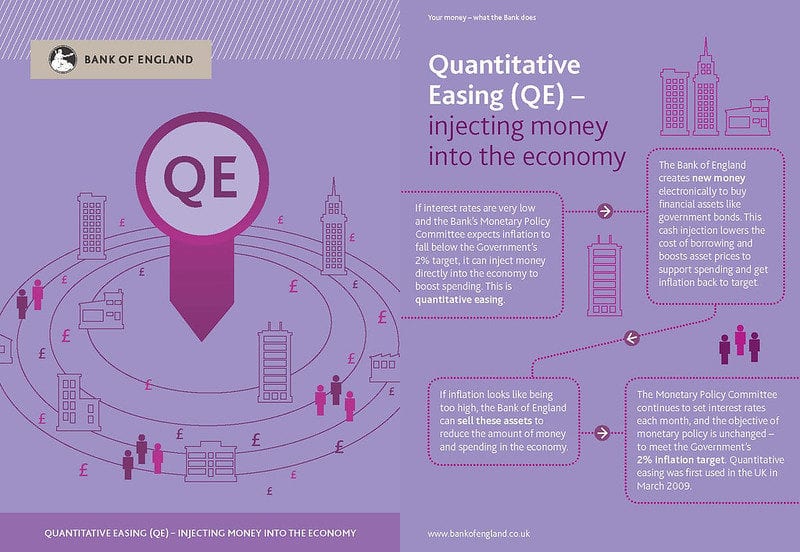
Quantitative easing, commonly referred to as QE, is a monetary policy tool used by central banks to stimulate the economy. It involves the central bank buying government bonds or other financial assets from commercial banks, which increases the money supply in the economy. The goal of QE is to encourage lending and investment, boost economic activity, and prevent deflation.
The Purpose of Quantitative Easing
The primary objective of quantitative easing is to stimulate economic growth and prevent or reverse a recession. By injecting additional money into the economy, central banks aim to lower interest rates and encourage borrowing and spending. This increase in spending can lead to higher business investment, job creation, and consumer spending, which can help stimulate economic activity.
Quantitative easing is typically used as a last resort when traditional monetary policy tools, such as adjusting interest rates, are no longer effective in boosting the economy. It is often employed during times of economic downturn or when there is a risk of deflation.
This image is property of www.kitco.com.
Quantitative Easing Process
The process of quantitative easing involves several steps. First, the central bank identifies the need for economic stimulus and determines the amount of money to be injected into the system. Then, the central bank purchases government bonds or other eligible securities from commercial banks. This increases the reserves held by banks, providing them with additional funds to lend.
When commercial banks receive payment for the bonds or securities they sold, they are more likely to lend money to businesses and individuals. This increased lending and investment can lead to economic growth and increased consumer spending.
How Does Quantitative Easing Affect the Economy?
Quantitative easing can have various effects on the economy, depending on the specific circumstances and the effectiveness of the policy implementation. Here are some of the potential impacts:
Lower Interest Rates
One of the primary goals of quantitative easing is to lower interest rates. As the central bank buys government bonds and other assets, the increased demand for these securities drives their prices up and their yields down. Lower bond yields lead to lower interest rates on loans, including mortgages and business loans. This can incentivize borrowing, investment, and spending, which can stimulate economic activity.
Increased Money Supply
Quantitative easing effectively increases the money supply in the economy. By purchasing bonds from commercial banks, the central bank injects money into the system, which increases the reserves held by banks. This increase in reserves can provide banks with more funds to lend, supporting increased lending and economic growth.
Asset Price Inflation
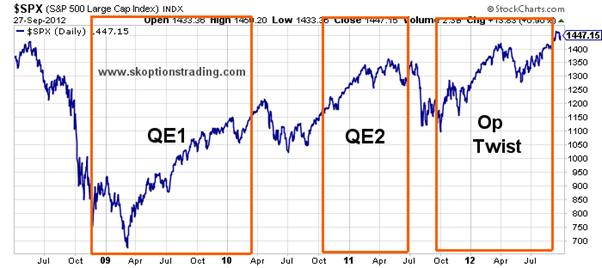
Quantitative easing can also lead to asset price inflation, as the injection of additional money into the economy can drive up the prices of stocks, bonds, and other financial assets. This can benefit investors who hold these assets, but it can also create concerns about potential bubbles in asset valuations.
Weakened Currency
Another potential impact of quantitative easing is a weakened currency. When a central bank implements QE, it increases the money supply and lowers interest rates, which can make the currency less attractive to investors. As a result, the value of the currency may decline relative to other currencies, potentially boosting exports but increasing the cost of imported goods.
This image is property of www.kitco.com.
Impact of Quantitative Easing on Gold Prices
Gold has traditionally been considered a safe haven investment during times of economic uncertainty and inflation. The impact of quantitative easing on gold prices can be attributed to several factors:
Inflationary Pressures and Gold
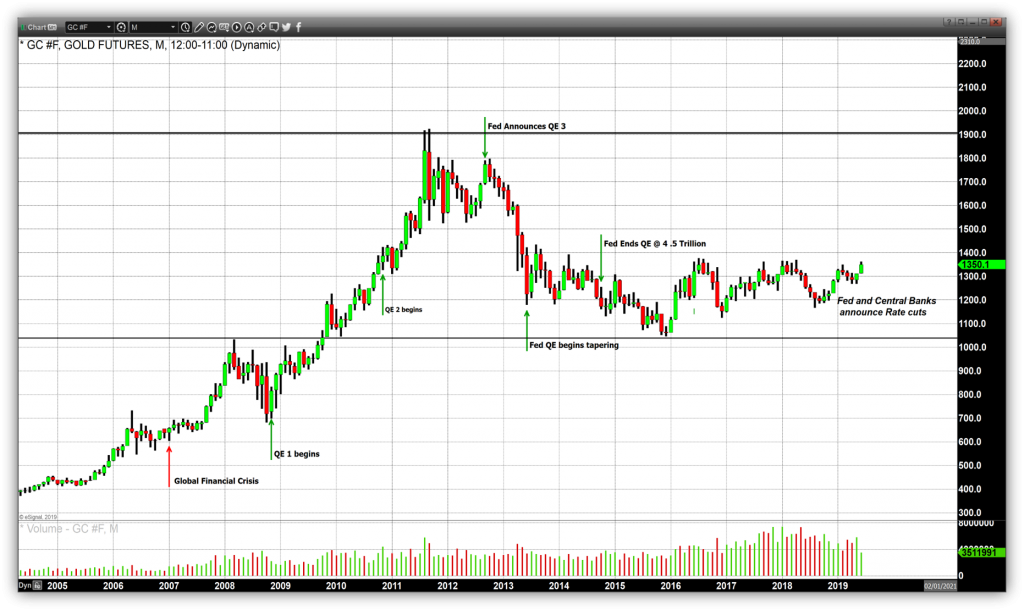
Quantitative easing, by increasing the money supply, can potentially lead to inflationary pressures. As the value of paper currency decreases, investors may seek to preserve their wealth by investing in assets that are seen as stores of value, such as gold. This increased demand for gold can drive up its price.
Interest Rates and Gold
Lower interest rates resulting from quantitative easing can make gold more attractive as an investment. Gold does not pay interest or dividends, so when interest rates are low, the opportunity cost of holding gold decreases. Investors may choose to allocate more of their portfolio to gold as a way to preserve their wealth and hedge against potential economic risks.
Currency Devaluation and Gold
If quantitative easing leads to a weaker currency, investors may turn to gold as a hedge against currency devaluation. Gold is often seen as a hedge against fiat currency depreciation, as its value is not directly tied to any particular currency. This perceived stability can make gold an attractive investment during periods of currency devaluation.
Market Sentiment and Gold
Market sentiment can also play a role in the impact of quantitative easing on gold prices. If investors perceive quantitative easing as a sign of economic instability or uncertainty, they may flock to gold as a safe haven investment. This increased demand can drive up gold prices.
Conclusion
Quantitative easing is a monetary policy tool used by central banks to stimulate economic growth and prevent or reverse a recession. While its impact on the economy can vary depending on the specific circumstances, it generally aims to lower interest rates, increase the money supply, and encourage lending and investment. The impact of quantitative easing on gold prices can be influenced by factors such as inflationary pressures, interest rates, currency devaluation, and market sentiment. As an investor, understanding the potential effects of quantitative easing on gold prices can help inform your investment decisions and risk management strategies.

This image is property of www.physicalgold.com.



