Alright, folks, let’s talk about everyone’s favorite shiny, precious metal: gold! Today, we’re diving into the age-old debate of whether gold is truly the best investment option when it comes to protecting your wealth against inflation. As an experienced investor in gold, I’ve spent years studying and observing the market, so I can confidently compare gold to other popular inflation hedges like real estate, stocks, and bonds. Buckle up, because we’re about to explore the pros and cons of each investment option, helping you make an informed decision about where to park your hard-earned money.
This image is property of static.seekingalpha.com.
Introduction
Welcome to my comprehensive guide on inflation and the different investment options available to hedge against it. Inflation can have a significant impact on your investments, and understanding how to protect your portfolio is crucial. In this article, we will explore the concept of inflation, its causes, and its effects on investments. We will then delve into various inflation hedges, such as gold, real estate, stocks, and bonds, discussing their historical performance and the factors influencing their returns during inflation. Finally, we will explore diversification strategies and risk factors to consider when building an inflation-proof portfolio.
1. Understanding Inflation
1.1 What is inflation?
Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time. Put simply, it means that your money’s purchasing power decreases as prices rise. Inflation is measured using various indices, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the Producer Price Index (PPI). Central banks often strive to maintain a moderate level of inflation to promote economic growth and stability.
1.2 Causes of inflation
Inflation can be caused by several factors, including:
- Demand-pull inflation: When there is excessive demand for goods and services, pushing prices higher.
- Cost-push inflation: When the cost of production rises, leading to increased prices.
- Monetary inflation: When there is an increase in the money supply, causing prices to rise.
Understanding the root causes of inflation can help investors make informed decisions about which assets to invest in to protect against its effects.
1.3 Effects of inflation on investments
Inflation can erode the value of your investments over time. It impacts both the returns you earn and the purchasing power of those returns. As the price of goods and services rises, the real value of your investment decreases. Investments that do not keep pace with inflation can result in a loss of wealth over the long term. It is, therefore, crucial to consider inflation when making investment decisions.
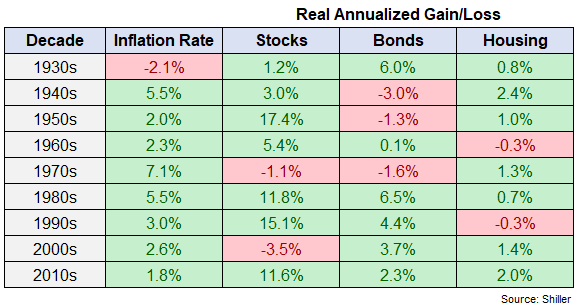
This image is property of awealthofcommonsense.com.
2. Importance of Inflation Hedges
2.1 The need for inflation hedges
Inflation hedges are assets that tend to hold or increase their value during periods of rising prices. These assets act as a shield against the erosion of purchasing power and can help preserve the value of your investments. Inflation hedges are particularly important for long-term investors seeking to safeguard their wealth against the effects of inflation.
2.2 How inflation hedges protect investments
Inflation hedges protect investments by either maintaining their value or increasing in price during inflationary periods. These assets often have intrinsic value, limited supply, or a strong historical track record of preserving wealth. By diversifying your portfolio with inflation hedges, you can potentially offset any losses caused by inflation and even generate positive returns.
3. Gold as an Inflation Hedge
3.1 Why invest in gold?
Gold has long been considered a reliable store of value and a hedge against inflation. It is a tangible asset that has been highly sought-after throughout history. Investing in gold allows you to hold an asset that has maintained its purchasing power over time, acting as a safe haven during times of economic uncertainty.
3.2 Historical performance of gold as an inflation hedge
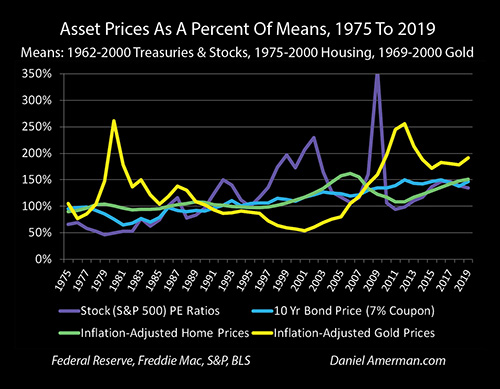
Historically, gold has shown a strong correlation with inflation, making it an attractive hedge. During periods of high inflation, gold prices have tended to rise. For example, during the 1970s, a decade characterized by high inflation, gold experienced significant price appreciation. This historical performance highlights gold’s potential as an effective inflation hedge.
3.3 Factors that influence the price of gold
Several factors influence the price of gold, including:
- Supply and demand dynamics: Limited supply and increased demand can drive up the price of gold.
- Economic and geopolitical conditions: Uncertainty and unrest often lead investors to seek the safety of gold, driving its price higher.
- Interest rates: Low or negative real interest rates can make gold more attractive as an investment.
Understanding these factors can help investors make informed decisions when considering gold as an inflation hedge.
3.4 Advantages and disadvantages of investing in gold
Investing in gold has its advantages, such as its historical track record as an inflation hedge and its liquidity. However, it also has disadvantages, including the lack of income generation and the potential for price volatility. It is essential to consider these pros and cons when incorporating gold into your investment strategy.
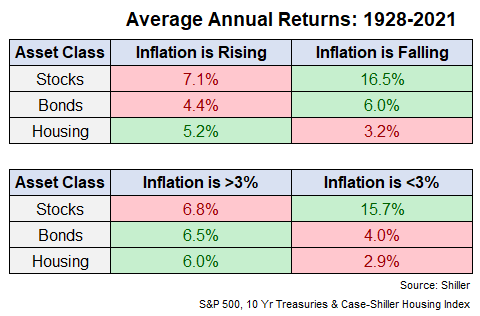
This image is property of awealthofcommonsense.com.
4. Real Estate as an Inflation Hedge
4.1 Investment opportunities in real estate
Real estate offers investors the opportunity to benefit from both income generation and potential price appreciation. It is a tangible asset that can serve as a store of value during periods of inflation. Investing in real estate can provide a steady stream of rental income and the potential for capital gains over the long term.
4.2 Real estate as a tangible asset
Unlike financial assets, real estate is a physical asset that can provide a sense of security and stability. During periods of inflation, the value of real estate tends to rise, providing a potential hedge against rising prices. Additionally, rental income from real estate can keep pace with inflation, allowing investors to maintain their purchasing power.
4.3 Historical performance of real estate as an inflation hedge
Historically, real estate has shown a strong correlation with inflation, making it an attractive hedge. During periods of high inflation, property prices typically rise, providing investors with a source of capital appreciation. However, it is essential to note that the performance of real estate can vary depending on various factors, such as location and market conditions.
4.4 Factors affecting real estate investments
Several factors can influence the performance of real estate investments, including:
- Location: Properties in desirable locations tend to appreciate more rapidly.
- Supply and demand dynamics: Limited supply and high demand can drive up property prices.
- Interest rates: Low-interest rates can make real estate more affordable, increasing demand.
- Economic conditions: Overall economic growth and stability can impact real estate values.
Understanding these factors is crucial when considering real estate as an inflation hedge.
4.5 Pros and cons of investing in real estate
Investing in real estate offers advantages such as potential income generation, capital appreciation, and diversification. However, it also has disadvantages, including illiquidity and the need for substantial upfront capital. It is essential to weigh these pros and cons before making real estate part of your investment strategy.
5. Stocks as an Inflation Hedge
5.1 Investing in stocks as an inflation hedge
Stocks represent ownership in companies and can offer investors a hedge against inflation. Companies can increase prices to keep up with rising costs, leading to potential stock price appreciation. Additionally, stocks have the potential to generate dividends, providing income that can keep pace with inflation.
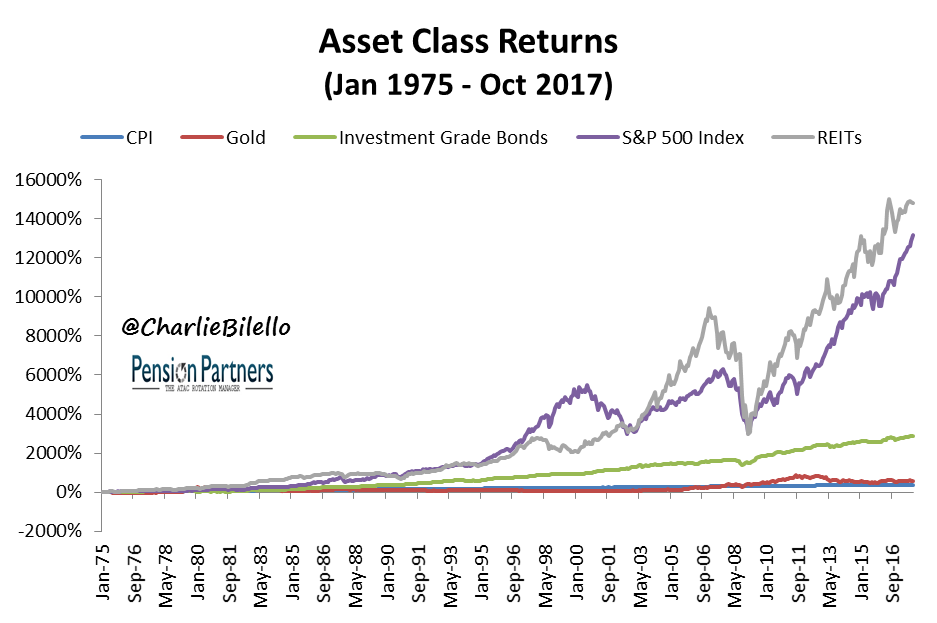
5.2 Historical performance of stocks as an inflation hedge
Historically, stocks have proven to be an effective hedge against inflation over the long term. While short-term market fluctuations can occur, stocks have generally outperformed inflation rates over extended periods. This is due to companies’ ability to adjust their prices and generate profits during inflationary periods.
5.3 Factors influencing stock market returns during inflation
Several factors can influence stock market returns during inflation, including:
- Industry dynamics: Some industries may be better positioned to weather inflationary pressures.
- Company profitability: Companies with strong profitability and pricing power may outperform during inflation.
- Interest rates: Interest rate hikes during inflation can impact stock valuations.
Understanding these factors can help investors make informed decisions when considering stocks as an inflation hedge.
5.4 Advantages and disadvantages of investing in stocks
Investing in stocks offers advantages such as potential capital appreciation, dividends, and ease of liquidity. However, it also carries risks, including market volatility and the potential for individual company underperformance. It is crucial to consider these pros and cons when incorporating stocks into your investment strategy.
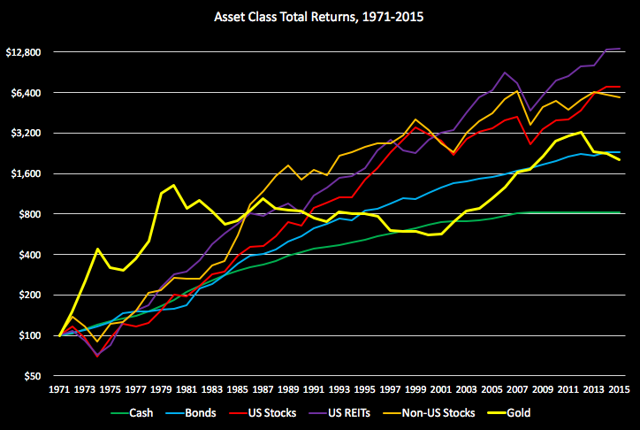
This image is property of gfmasset.com.
6. Bonds as an Inflation Hedge
6.1 Understanding bonds and their role as an inflation hedge
Bonds are fixed-income securities issued by governments, municipalities, or corporations. They can play a role in a balanced investment portfolio and act as an inflation hedge under certain circumstances. Inflation-indexed bonds, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), offer investors protection against rising prices by adjusting their principal and interest payments with inflation.
6.2 Historical performance of bonds during inflation
Historically, bonds have shown mixed performance during inflationary periods. While inflation-indexed bonds can provide a reliable hedge, traditional fixed-rate bonds may experience a decrease in their inflation-adjusted value. Investors should carefully consider the type of bonds they hold when seeking protection against inflation.
6.3 Types of bonds to consider
Different types of bonds can be considered when building an inflation-hedged portfolio:
- Inflation-indexed bonds: These bonds adjust their principal and interest payments with inflation, offering protection against rising prices.
- Municipal bonds: Municipal bonds are issued by states, cities, or other local governments and can provide income and potential tax advantages.
- Corporate bonds: Corporate bonds carry higher credit risk but can offer higher yields compared to government bonds.
Understanding the characteristics of different types of bonds can help investors tailor their portfolio to their specific needs.
6.4 Factors affecting bond returns during inflation
Several factors can influence bond returns during periods of inflation, including:
- Interest rates: Rising interest rates can lead to a decrease in bond prices.
- Credit risk: Economic downturns during inflation can affect the creditworthiness of bond issuers.
- Inflation expectations: If inflation exceeds market expectations, bond yields may not keep pace, impacting returns.
Considering these factors is crucial when incorporating bonds into an inflation-hedged portfolio.
6.5 Pros and cons of investing in bonds
Investing in bonds offers advantages such as income generation, defined maturity dates, and a range of risk profiles. However, it also has disadvantages, including interest rate risk and credit risk. It is essential to carefully consider these pros and cons before incorporating bonds into your investment strategy.
7. Diversification Strategies
7.1 Importance of diversification
Diversification is a risk management strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors. It aims to reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on the overall portfolio. Diversifying your portfolio with a combination of asset classes, such as gold, real estate, stocks, and bonds, can help mitigate risks and enhance potential returns.
7.2 Combining gold, real estate, stocks, and bonds
Each asset class has its own unique characteristics and risks. Combining these asset classes in a diversified portfolio allows investors to benefit from their individual strengths and potentially offset weaknesses. For example, while gold and real estate can act as hedges against inflation, stocks and bonds can provide income and capital appreciation potential.
7.3 Portfolio allocation strategies
Diversification requires careful portfolio allocation. Investors must determine the appropriate allocation percentages based on their risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions. Allocating assets across different inflation hedges can provide a balance between risk and return, helping to protect against the negative effects of inflation.
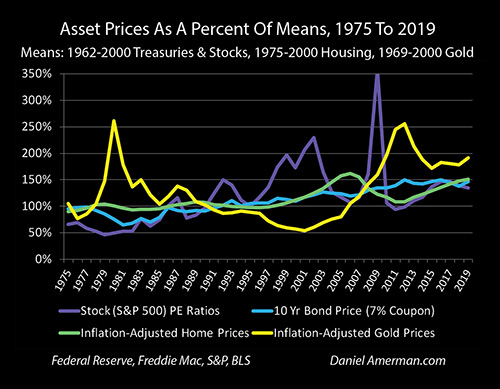
This image is property of danielamerman.com.
8. Risk Factors to Consider
8.1 Volatility and liquidity
Investing in any asset class carries inherent risks, including volatility and liquidity concerns. Some investments, such as stocks and gold, can be more volatile, experiencing significant price fluctuations. Additionally, certain assets, like real estate, may have limited liquidity, making it challenging to quickly sell or exit a position. It is important to assess and manage these risks when constructing an inflation-proof portfolio.
8.2 Economic and geopolitical risks
Economic and geopolitical factors can have a profound impact on investments. Changes in government policies, global trade dynamics, or geopolitical events can create uncertainty and affect the performance of inflation hedges. Staying informed about these risks and considering their potential impact on your investments is crucial when building an inflation-proof portfolio.
8.3 Inflation expectations
Inflation expectations play a significant role in investment decisions. Market expectations for future inflation levels can influence both asset prices and investment returns. Monitoring inflation indicators and staying abreast of economic data can help investors adjust their portfolio allocations based on expected inflation levels.
9. Conclusion
Inflation poses a significant risk to the value of your investments. To hedge against the erosion of purchasing power, it is essential to consider assets that have historically performed well during inflationary periods. Gold, real estate, stocks, and bonds all offer unique advantages as inflation hedges, and their inclusion in a diversified portfolio can help protect against the negative effects of inflation. Understanding the characteristics, risks, and performance history of these assets is crucial when constructing an investment strategy tailored to your needs. By carefully considering inflation hedges and diversifying your investments, you can work towards building a portfolio that can withstand the impact of inflation and potentially grow your wealth over the long term.